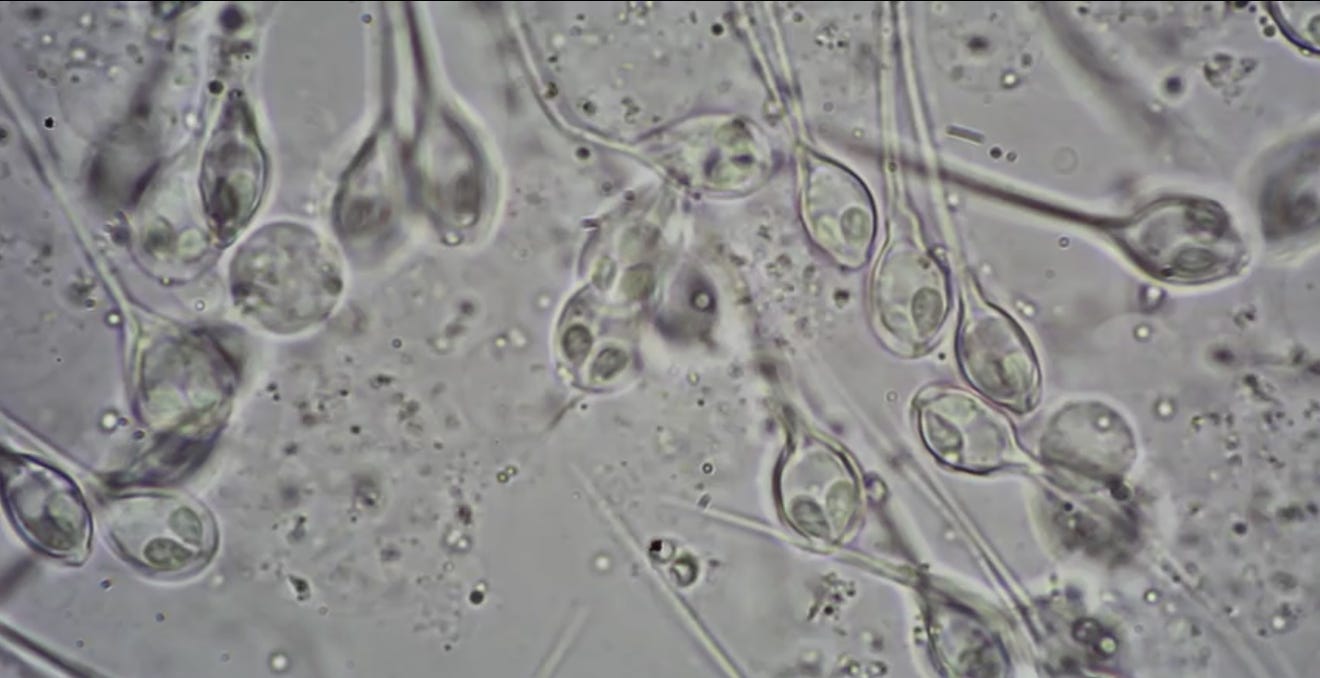
Though many single-celled lifeforms have evolved to survive without oxygen, multicellular organisms have always been believed to need it to live. Now, scientists in Tel Aviv, Israel, have found that Henneguya salminicola, a parasite, which spends its life attached to the muscle tissue of fish, has adapted to living without oxygen.
Dorothee Huchon, a molecular geneticist at Tel Aviv University, and her colleagues stumbled upon the discovery accidentally while investigating the mitochondrial genes of the tiny H. salminicola, which comprises fewer than ten cells. Commonly dubbed "the powerhouse of the cell," mitochondrion help break down the oxygen we breathe in to create adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a chemical that provides the energy needed for many of the fundamental processes of living cells, including muscle contraction.
However, when the researchers stained the H. salminicola cells with a blue fluorescent dye that binds to DNA, they found no DNA visible in cells outside the nucleus. In contrast, the same test on some closely-related parasites revealed tiny blue dots corresponding to mitochondrial genomes outside the nucleus. Though further investigation revealed structures resembling mitochondria in the H. salminicola, they were incapable of producing the enzymes needed for respiration.
"We don't know why H. salminicola has lost this ability while all of its immediate relatives that we have identified use oxygen. As these parasites move through their life cycle, they may also live inside a worm host where they would have to make do with virtually no oxygen, as well. The worm host of H. salminicola has never been identified, but it too may live in sediments with very low oxygen levels," says Prof. Huchon.

The Tel Aviv scientists, who published their findings in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on February 10, 2020, are still unsure how H. salminicola generates energy. "It's not yet clear to us how the parasite generates energy," Prof. Huchon says. "It may be drawing it from the surrounding fish cells, or it may have a different type of respiration such as oxygen-free breathing, which typically characterizes anaerobic non-animal organisms."
Regardless of the mechanism used, the professor believes the discovery is extremely significant for evolutionary research. "It is generally thought that during evolution, organisms become more and more complex, and that simple single-celled or few-celled organisms are the ancestors of complex organisms," she says. "But here, right before us, is an animal whose evolutionary process is the opposite. Living in an oxygen-free environment, it has shed unnecessary genes responsible for aerobic respiration and become an even simpler organism."
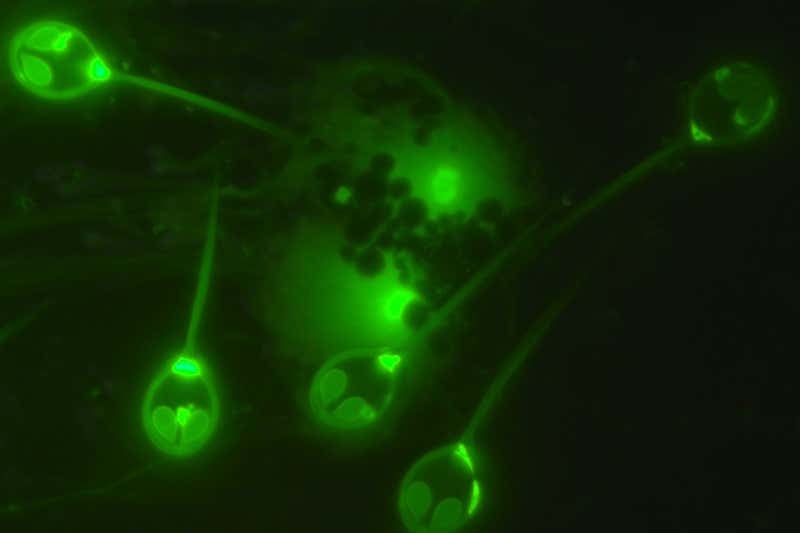
A distant cousin of the jellyfish, H. salminicola is a fairly common parasite that causes white cysts, or "tapioca disease," on the flesh of fish, such as the adult Chinook and the coho salmon. Though unsightly, the tiny bubbles, which ooze a creamy white liquid filled with many microscopic myxozoan spores when ruptured, are generally harmless to humans and the fish itself.
Resources: www.aftau.org, Cnet.com, www.newscientist.com
